Lifting Overhead: All You Need to Know
Author:
Reviewed by:
(21 years of Oly Lifting experience)
Unlock your full potential by engaging with our experts and community! Have questions about your fitness journey or looking for expert advice on weightlifting techniques? Don’t hesitate — leave a comment below and Sergii Putsov will provide a personalized answer and insights to help you reach your goals.
Torokhtiy is reader-supported. Some links are affiliate links, and we may earn a commission at no extra cost to you. See our disclosure page for details.
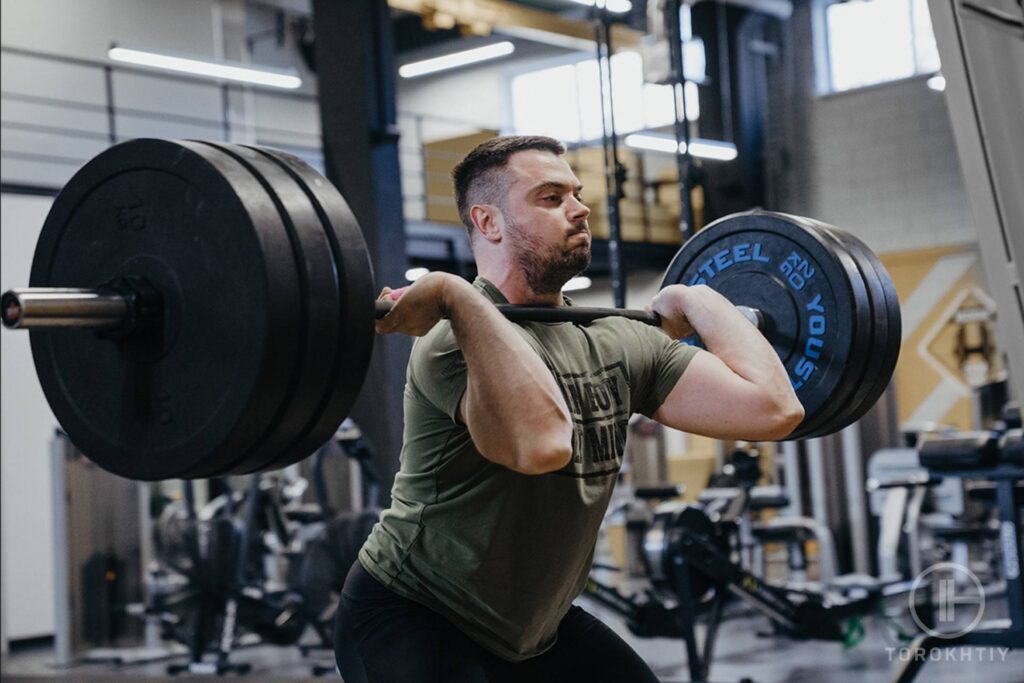
Overhead lifting is common in various weightlifting, fitness, and mobility workouts.
However, lifting weight overhead is common in our daily lives too, such as when we lift various objects up and down.
Here are some expert tips and exercises for keeping your upper body safe and mobile and developing your overhead lift.
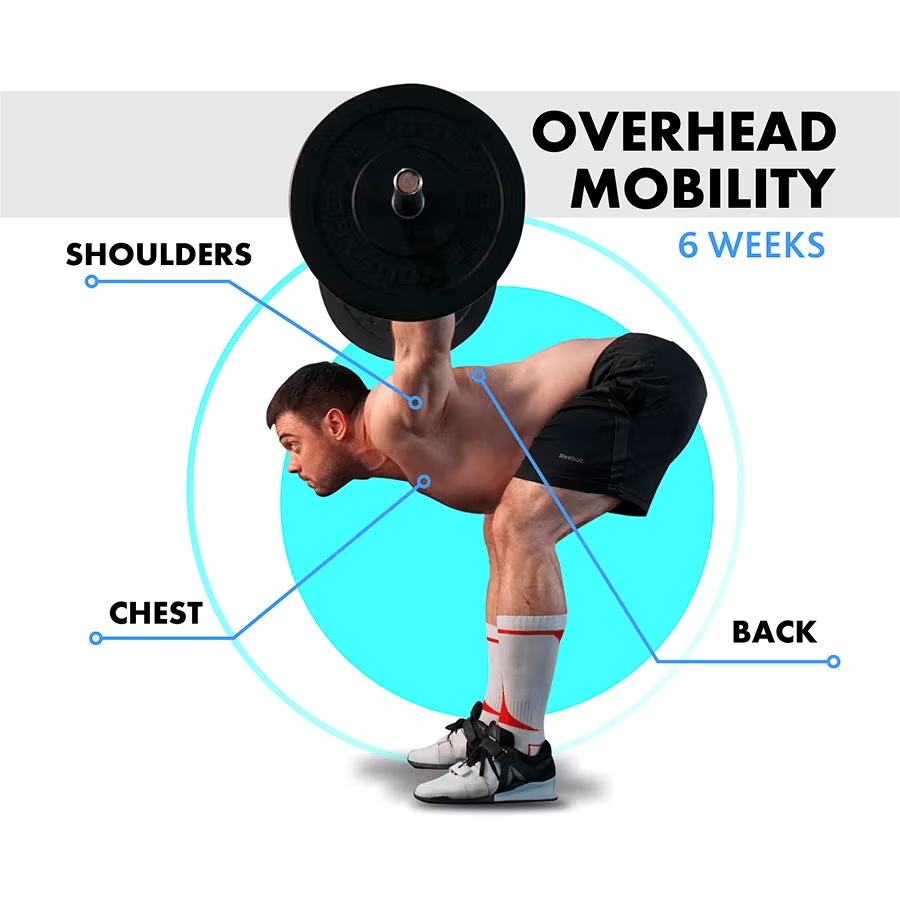
Practicing lifting overhead is important for upper body mobility. Low mobility in arms and shoulders can stop you from performing some highly recommended exercises. However, even if you’re not an athlete, overhead mobility practice is important for your quality of life and helps you avoid issues that come with age.

What Is Lifting Overhead?
Overhead lifting refers to lifting and balancing an object over the head, typically with the arms fully extended. It’s most commonly associated with weight lifting exercises, such as variations of the Snatch or Press.
However, it also refers to everyday activities that result in the same motion.
Should You Be Lifting Overhead?
Overhead weight lifting is a great exercise for upper body strength and mobility. Doing overhead lifting can prevent common shoulder, upper back, and arm issues that occur as we age, such as chronic pain.
However, lifting weight overhead causes pressure on shoulder joints and wrists, so it’s best to avoid it for people with known issues in these areas – unless approved by a medical expert.
Why Overhead Mobility Matters in Weightlifting
Without proper overhead mobility, weightlifters may struggle to perform key movements with proper form, limiting their performance potential and increasing their risk of injury.
3 Types Of Barbell Overhead Lifts
Strict Overhead Press (Military Press)
The strict overhead press, also known as the military press, is the most basic and well-known overhead lifting exercise. Preferably, it’s done using a barbell, although dumbbells or kettlebells can be used as a substitute. The movement engages multiple muscle groups – primarily the shoulders, triceps, and upper back – making this a popular exercise for overall upper body strength. To do a Standard Overhead/Military Press, stand up straight with your feet spread in line with your hips and shoulders.
Rest the barbell just above your chest area either by lifting it from the ground or by grabbing below it from a standing rack. Grip the barbell with your hands spread slightly wider than your shoulder width, with your elbows pointing slightly outward (front squat position). Tighten your core and press the bar over your head to a full arm extension – the end position should be you standing straight from hand to toe, with the barbell held directly above your head with your hands. Stop for about one second at the height of your arm extension, then lower the bar back down the same path you lifted it up.
Push Press
The Push Press is another popular lifting overhead exercise and is very similar and often confused with the Military Press. The starting position is exactly the same – feet at hip/shoulder width, barbell resting on top of your torso, hands gripping under the bar, elbows pointed slightly outwards.
However, the difference is that during the Military Press we are strictly standing still, while in the Push Press we’re going to use our legs to add more force. From the starting position, keep your feet glued to the ground and start bending your knees downwards as if going into a squat, maintaining your upper body straight.
Slightly before your legs are bent halfway, rapidly push yourself back up by extending your legs back into a standing position. To know if you’ve bent your knees to the correct position, simply feel your hips. If your upper body feels like it’s “sitting” on your hips – the majority of your upper body pressure is on them and your knees are no longer stressed – you’re in the right spot.
Using this momentum, push against the floor from the full foot and then lift your heels slightly off the ground (stand on your toes) and, at the same time this is happening, push the barbell above your head the same as you would in a Military Press.
The end position and reset motion are exactly the same between the two exercises.
Push Jerk / Power Jerk
The Push Jerk is an important exercise for professional overhead weight lifting as it is one of the main components of the Clean & Jerk – a competitive weightlifting exercise found everywhere from amateur lifting competitions to the Olympic Games. To perform a Push/Power Jerk, you start by repeating the exact same motion as a Push Press, except you’re going to add a slight hop when pushing back up.
This time, instead of standing on your toes, let the exercise momentum pull you up slightly off the ground. Your feet should naturally lift slightly off the ground as you extend your arms above your head. The height of the hop will differ for each athlete, but realistically it shouldn’t be higher than an inch, your feet should barely leave the ground. Land with your full feet back into a half squat position – knees bent, feet spread slightly more than your hip width – with your hands holding the barbell straight above your head.
Pause for half a second to a second, then extend your legs to return back into a standing position. Reset your foot position back into the hip/shoulder line, then let down the barbell back onto your torso while fully controlling its descent.
Shoulder Mobility Problems
Shoulder mobility problems can affect everything from your ability to do everyday activities to properly exercising. Here are some of the most common medical issues associated with them.
Frozen shoulder
Medically known as adhesive capsulitis, manifests as pain and stiffness in the shoulder joint, making it difficult to move the arm. According to research, shoulder pain affects 18-26% of adults during their life, with an increased chance of occurrence if their occupation requires heavy lifting.
Follow us!

Free!
Get a 2-week Weightlifting Program as a bonus for the subscription to kickstart your training plan!

Free!
Rotator Cuff Tear
Rotator cuffs are a group of four muscles and tendons that stabilize your shoulder joint. As the name suggests, the primary motion that engages them is arm rotation.
Across the U.S., two million people each year visit the doctor as a result of rotator cuff tears. Apart from pain in the shoulders, rotator cuff tear can result in lower arm mobility.
Shoulder Arthritis
Arthritis occurs due to the wearing down of the joint connective tissue called Cartilage.
This injury is common for athletes and workers who perform overhead lifting as part of their daily life.
The danger of Arthritis is that it is permanent, and even medication and surgery can only provide temporary solutions to pain and loss of mobility. Shoulders are the third most common joint affected by arthritis, after hips and knees.

5 Overhead Stability Exercises To Increase Shoulder Strength
Depending on your athletic level, it’s recommended to do these exercises 8-12 reps in 3-4 sets.
Overhead Press
The basic shoulder workout you see at the gym, most commonly done while standing or sitting with your back straight.
Start by holding a dumbbell or kettlebell at shoulder level. Push it overhead in a straight line from your shoulder above your head, then follow the same path back down controlling the weight.
Standing Lateral Raise
Start by standing with your feet shoulder-width apart. Extend your arms down to your hips. Raise your arms sideways, keeping them straight until they’re horizontal to the ground.
The exercise can be done weightless or using a dumbbell, kettlebell, or resistance band.
Shoulder Blade Squeeze
A simple exercise that you can do at home without equipment. Start by standing with your feet about shoulder-width apart. Pinch your shoulder blades together and hold that position for a few seconds.
This exercise is commonly used with resistance bands or workout tubes for added resistance. hooking them in front of you for a fixed rack as an option.
Y Raise
Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart. Raise your arms to form a “Y” shape, then lower them back to the starting position. You can use a light weight for added resistance.
Plank With Arm Raises
Start from a plank position with your arms straight. Going one at a time, raise your arm up and in front following a 90-degree angle, and hold it up for a few seconds.
Use a light weight or resistance band to increase difficulty.
FAQ
Are Overhead Lifts Safe?
Overhead lifting is safe as long as you don’t have a medical condition, such as chronic pain, that prevents you from doing it.
Do Overhead Lifts Build Muscle?
Overhead lifts are excellent muscle-building exercises as they activate multiple upper body parts, such as your arms, shoulders, and back, at the same time.
Conclusion
Practicing lifting weight overhead not only helps you in weightlifting, it improves your everyday life. Regular shoulder mobility exercises can help you avoid many physical issues that result from daily activities and aging.
Are you satisfied with your shoulder mobility? Do you practice overhead lifts regularly?
Let me know in the comments and make sure to follow my social media for more exercise tips and other fitness content.
Also read:
- Upper Body Stretch
- Lower Back Mobility Exercises
- Athlete Mobility Workout
- Snatch Mobility
- Overhead Squat Assessment
- Trapezius Stretches
- Tricep Stretches
- Prilepin’s Chart Guide: Optimize Your Lifts
- Arm Exercises for Weightlifting: Are They Important?
- How To Get Bigger Wrists: Growth Strategies & Exercises
References:
- Weightlifting in Olympics: Everything you need to know // Olympics: https://olympics.com/en/news/weightlifting-olympics-rules-history-snatch-clean-and-jerk
- SHOULDER DISORDERS AND OCCUPATION // National Library of Medicine: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4836557/
- Rotator Cuff Tears // Orthoinfo: https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/rotator-cuff-tears/
- Cartilage // Cleveland Clinic: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/23173-cartilage#:~:text=What%20is%20cartilage%3F,when%20you%20use%20your%20joints.
- Arthritis of the Shoulder // Hospital for Special Surgery: https://www.hss.edu/condition-list_arthritis-shoulder.asp
Why Trust Us?
With over 20 years in Olympic weightlifting, strength training, nutrition coaching, and general fitness our team does its best to provide the audience with ultimate support and meet the needs and requirements of advanced athletes and professional lifters, as well as people who strive to open new opportunities and develop their physical capabilities with us.
By trusting the recommendations of our certified experts in coaching, nutrition, and sports training programming, as well as scientific consultants, and physiotherapists, we provide you with thorough, well-considered, and scientifically proven content. All the information given in the articles concerning workout programming, separate exercises, and athletic performance, in general, is based on verified data.
The product testing process is described in more detail here.
Author: Sergii Putsov
Head of Sport Science, PhD
Best Results: Snatch – 165 kg,
C&J – 200 kg
Sergii Putsov, Ph.D., is a former professional weightlifter and National team member, achieving multiple medals in the 94 kg weight category at national competitions. With a Master’s degree in “Olympic & Professional Sport Training” and a Sport Science Ph.D. from the International Olympic Academy, Greece, Sergii now leads as the Head of Sport Science. He specializes in designing training programs, writing insightful blog articles, providing live commentary at international weightlifting events, and conducting educational seminars worldwide alongside Olympic weightlifting expert Oleksiy Torokhtiy.
Reviewed by: Oleksiy Torokhtiy
Olympic Weightlifting Champion, PhD in Sport Science
Best Results: Snatch – 200 kg,
C&J – 240 kg
Oleksiy Torokhtiy is a professional athlete boasting 20 years of experience in Olympic weightlifting. With multiple European and World titles under his belt, he has showcased his prowess in two Olympic Games (Beijing 2008 and London 2012). Upon concluding his illustrious career, Oleksiy dedicated himself to coaching. By 2022, he had conducted over 200 weightlifting seminars worldwide. He is the visionary behind an international sportswear and accessories brand known for its motto, “Warm Body Cold Mind.” Additionally, he is an esteemed author and the creator of a series of training programs and eBooks.




Still have questions after reading our article? Unlock your full potential by engaging with our experts and community! Don’t hesitate — leave a comment below and Sergii Putsov will provide a personalized answer and insights to help you reach your goals.