Push Press
Author:
Unlock your full potential by engaging with our experts and community! Have questions about your fitness journey or looking for expert advice on weightlifting techniques? Don’t hesitate — leave a comment below and Oleksiy Torokhtiy will provide a personalized answer and insights to help you reach your goals.
Torokhtiy is reader-supported. Some links are affiliate links, and we may earn a commission at no extra cost to you. See our disclosure page for details.
What is a Push Press?
Push press is a compound exercise that involves pressing a weight overhead while utilizing a slight knee bend and explosive upward thrust to drive the weight upward. It is commonly performed with a barbell or dumbbells and is a popular exercise for building upper body strength and power.
What Muscles are Working in Push Press?
The barbell push press is a compound exercise that primarily targets the shoulder muscles, specifically the anterior and lateral deltoids. However, it also recruits several other muscle groups, including the triceps, upper chest, and upper back muscles.
So what does push press work?
1. Shoulder Muscles:
The shoulder muscles, also known as deltoids, play a significant role in the push press exercise. The anterior deltoid, located at the front of the shoulder, is responsible for lifting the weight in front of the body during the push press. The lateral deltoid, located at the side of the shoulder, helps lift the weight overhead.
2. Triceps:
The triceps, located at the back of the upper arm, work in conjunction with the shoulders to help lift the weight overhead during the push press. They are responsible for extending the elbow joint.
3. Upper Chest:
The upper chest muscles, also known as the clavicular head of the pectoralis major, assist in the lifting of the weight overhead. They help stabilize the shoulders and contribute to the overall power generated by the upper body during the push press.
4. Upper Back:
The upper back muscles, including the traps and rhomboids, also play a crucial role in the push press exercise. They help stabilize the shoulders and scapulae, allowing for proper alignment and optimal force transfer during the exercise.
5. Core Muscles:
The core muscles, including the abs, obliques, and lower back muscles, play a vital role in the push press exercise. They help stabilize the torso and transfer force from the lower body to the upper body. This allows for a more efficient transfer of power and helps reduce the risk of injury to the lower back.
6. Legs:
The legs play a crucial role in the push press, as they provide the explosive power needed to lift the weight overhead. The quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes all work together to generate force and help drive the weight upward during the exercise.
Overall, the push press exercise is a full-body exercise that targets multiple muscle groups simultaneously. It is an efficient way to build upper body strength and power while also improving overall athleticism and functional fitness.
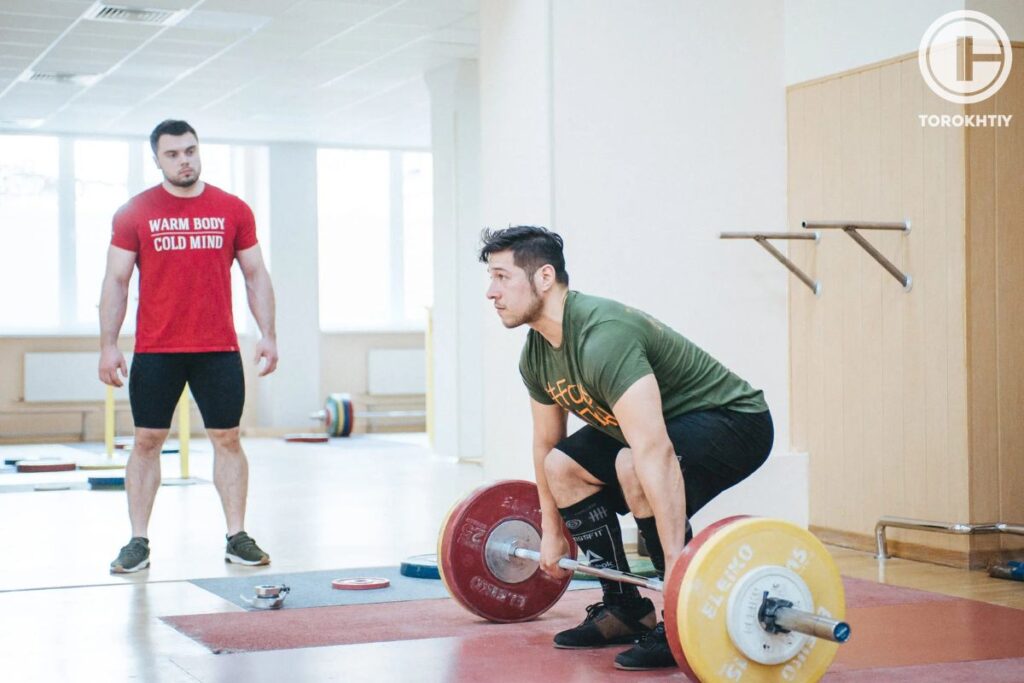

How to Perform Push Press?
To perform the overhead push press with a barbell, you should follow these steps:
Step 1: Begin by standing with your feet shoulder-width apart and your toes pointing slightly outward. Place the barbell across the front of your shoulders, with your palms facing forward and your elbows pointing down.
Step 2: Slightly bend your knees, then explode upward by driving your legs into the ground. As you do this, press the weight overhead, using the momentum from your legs to help lift the weight.
Step 3: At the top of the lift, fully extend your arms and push the weight overhead until your elbows are locked out. Hold this position briefly before lowering the weight back down to your shoulders.
Step 4: Lower the weight back down to your shoulders in a controlled manner, then repeat the exercise for the desired number of reps.
It is important to note that proper push press form is crucial when performing the push press, as improper form can lead to injury and reduce the effectiveness of the exercise. This is why it is so important how to push press.
Push Press Pros and Cons
Pros:
✅ The standing push press is an efficient exercise for developing upper body strength and power.
✅ It targets multiple muscle groups, including the shoulders, triceps, upper chest, and upper back muscles.
✅ It also involves the legs, making it a full-body exercise that can help increase overall strength and power.
✅ The push press can be modified to suit different fitness levels and goals.
Cons:
❌ Push press can be a challenging exercise to perform correctly, especially for beginners who may struggle with proper form and technique.
❌ It can also place a significant amount of stress on the shoulder joints, which may increase the risk of injury if performed incorrectly or excessively.
❌ Push press may not be suitable for individuals with pre-existing shoulder injuries or mobility issues.
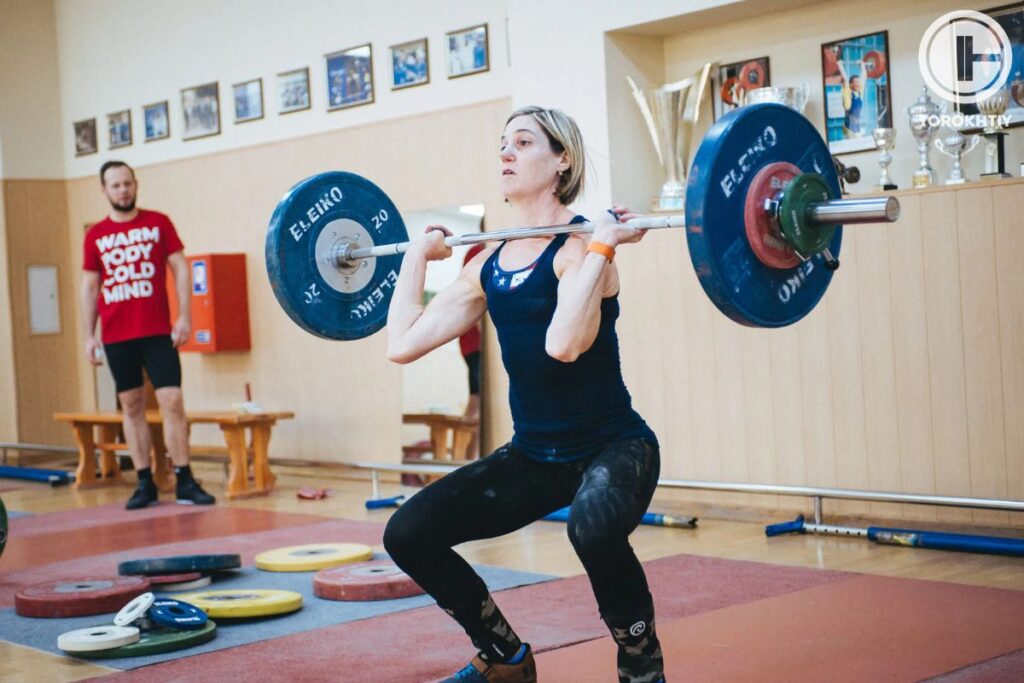
Main Mistakes in Push Press Execution
There are several common mistakes that people make when performing the push press exercise. These include:
❌ Rounding the back
Failing to lock out the elbows at the top of the lift can reduce the effectiveness of the exercise and increase the risk of injury.
❌ Not using the legs
Push press is a full-body exercise that requires the use of the legs to generate power. Failing to use the legs can make the exercise less effective and increase the risk of injury.
❌ Leaning too far forward
This can place excessive stress on the shoulders and reduce the effectiveness of the exercise.
Push Press Variations
The push press is a popular exercise in Olympic weightlifting and is often used to improve overhead strength and power. There are several variations of the push press that can be used to target different muscle groups, improve technique, and provide variety in training. Here are some of the most common push press variations in Olympic weightlifting:
1. Push Press with Moving onto the Toes
This variation of the push press involves more explosive components. With the detachment of heels, the athlete is able to make great efforts in the drive phase and perform the exercise with heavy weight.
2. Push Press on the Full Foot
When working from a full foot, the muscles of the arms are more loaded and, with this option, therefore, work on the upper limbs is more qualitative.

3. Behind the Neck Push Press
This variation involves performing the push press with the barbell behind the neck, rather than in front. This can be useful for improving mobility and flexibility in the shoulders and upper back.
4. Dumbbell Push Press
This variation involves performing the push press with dumbbells rather than a barbell. This can be useful for improving stability in each arm and can help improve overall athleticism and functional fitness.
5. Single Arm Push Press
This variation involves performing the push press with one arm at a time. This can be useful for improving unilateral strength and stability and can help address any imbalances between the left and right sides of the body.
6. The Functional Fitness Push Press
The Functional Fitness push press is a variation of the traditional push press that is commonly used in Functional Fitness workouts. The Functional Fitness push press takes this exercise a step further by adding a few unique features to increase its intensity. In the Functional Fitness push press, the lifter begins with the barbell or dumbbells resting on the front of the shoulders.
From this position, the lifter performs a slight dip in the knees to create momentum, and then uses this momentum to help drive the weight up overhead. While bringing the bar back on the shoulders, Functional Fitness athletes perform push press in so-called unbroke style, meaning that they don`t rest with the bar on their shoulders, but start to dip and drive immediately to lift the bar again and again.
One of the unique features of the Functional Fitness push press is that it is often performed as part of a larger workout or circuit, rather than as a standalone exercise. This means that the lifter may perform multiple sets of push presses in rapid succession, with little rest in between. This can help increase the intensity of the exercise and provide a cardiovascular challenge, in addition to building upper body strength and power.
Overall, these variations can be useful for adding variety to training, addressing weaknesses, and improving overall technique and athleticism in Olympic weightlifting.
Push Press Alternatives
While the push press is a highly effective exercise for building strength and power in the upper body, there may be situations where an alternative exercise is needed. Here are some push press alternatives for Olympic weightlifting and general population fitness:
1. Overhead Press
The overhead press, also known as the military press, is a classic exercise that targets the shoulder muscles and can be used as an alternative to the push press. It involves pressing the barbell overhead from a standing position without the use of leg drive. This exercise can be useful for improving overall shoulder strength and stability.

2. Dumbbell Overhead Press
This variation of the overhead press involves using dumbbells instead of a barbell. It can be useful for improving unilateral strength and stability and can help address any imbalances between the left and right sides of the body.
3. Arnold Press
The Arnold press is a variation of the dumbbell overhead press that involves rotating the arms during the press. This can be useful for targeting different areas of the shoulder muscles and improving overall shoulder mobility and flexibility.
4. Handstand Push-Up
The handstand push-up is a challenging bodyweight exercise that targets the shoulders and can be used as an alternative to the push press. It involves pressing the bodyweight overhead while in a handstand position against a wall or other stable surface. This exercise can be useful for improving overall upper body strength and power.
5. Clean and Press
The clean and press is a classic Olympic weightlifting exercise that involves lifting the barbell from the floor to the shoulders and then pressing it overhead. This exercise can be useful for improving overall upper body and lower body strength and power.
6. Thruster
The thruster is a combination exercise that involves performing a front squat followed by a push press. This exercise can be useful for improving overall leg and upper body strength and power and can be a useful accessory exercise for the snatch and clean and jerk.
Key Factors in Push Press Programming in Olympic Weightlifting
Programming the push press as part of an Olympic weightlifting program requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure maximum benefit and minimize the risk of injury. Here are some important factors to consider when programming the push press in Olympic weightlifting:
1. Technique
As with any Olympic weightlifting movement, proper technique is crucial for the push press. Coaches should ensure that lifters have a solid understanding of the correct foot and hand placement, dip and drive mechanics, and overhead position before incorporating push presses into their programming.

2. Volume
The volume of push presses in a training session or program should be carefully planned to avoid overuse injuries and promote recovery. This may involve gradually increasing the number of sets and reps over time, while also monitoring how the lifter responds to the exercise.
3. Frequency
The frequency of push presses in a training program should be balanced with other exercises and movements to ensure proper recovery and avoid overuse injuries. This may involve varying the frequency of push presses depending on the phase of training, such as focusing on higher volume and lower intensity during a hypertrophy phase, and lower volume and higher intensity during a strength or power phase.
4. Periodization
The push press can be programmed using periodization techniques, such as block periodization, to help ensure consistent progress over time. This may involve focusing on different aspects of the lift, such as increasing volume or intensity, during different training phases.
5. Assistance Exercises
Assistance exercises such as overhead squats, presses, and other variations of the push press can help improve technique, strength, and power in the lift. These exercises can be incorporated into a training program to help develop specific aspects of the push press and build a more well-rounded athlete.
The optimal ranges of sets, reps, and percentage of the clean & jerk for push press in Olympic weightlifting will vary based on the athlete’s training goals and current strength level. However, here are some general guidelines that can be used as a starting point:
6. Sets and Reps
For the push press, athletes should aim to perform 3-6 sets of 2-8 reps per session. The total number of sets and reps will depend on the athlete’s training phase and overall training volume.
7. Percentage & Intensity
The percentage of the clean & jerk that can be used for the push press will depend on the athlete’s strength level and training goals. As a general guideline, athletes should aim to use 60-90% of their 1RM clean & jerk for the push press. For example, if an athlete’s 1RM clean & jerk is 100 kg, they could use 60-90 kg for their push press.
The intensity of the push press should be appropriate for the athlete’s training phase and goals. During a strength phase, athletes may use higher percentages of their 1 RM clean & jerk for lower reps, while during a power or hypertrophy phase, athletes may use lower percentages of their 1 RM clean & jerk for higher reps.
8. Rest and Recovery
The rest period between sets of push press will depend on the athlete’s training goals and current level of fitness. As a general guideline, athletes should rest 1-3 minutes between sets to allow for adequate recovery.
It’s important to note that these ranges are only guidelines and should be adjusted based on the individual athlete’s goals, current strength level, and training phase.
Who Should Use Push Press Exercise?
The push press exercise is a versatile movement that can be used by a variety of individuals, from Olympic weightlifters to general fitness enthusiasts. Here are some groups of people who can benefit from incorporating the push press into their training program:

1. Olympic Weightlifters
The push press is a key movement in Olympic weightlifting and is used to develop strength and power in the shoulders, legs, and core. Weightlifters can use the push press to improve their overhead strength and to enhance their clean & jerk and snatch performance.
2. Powerlifters
Powerlifters can use the push press to develop upper body and leg strength, which can improve their bench press and squat performance.
3. Fuctional Fitness Athletes
The push press is a common movement in Fuctional Fitness workouts and is used to improve overall fitness and conditioning. Fuctional Fitness athletes can use the push press to develop shoulder and leg strength, and to improve their performance in other movements such as thrusters and overhead squats.
4. General Fitness Enthusiasts
The push press can be used by general fitness enthusiasts to develop upper body and leg strength, improve overall fitness, and increase muscle mass. It can also be used as a functional movement that can improve daily activities and reduce the risk of injury.
5. Athletes from Other Sports
The push press can be used by athletes from other sports such as basketball, football, and volleyball to improve their explosive power, jump height, and overall athleticism.
It’s important to note that the push press workout may not be suitable for individuals with certain injuries or limitations, such as shoulder pain or mobility issues.7.7.
Also Read:
Why Trust Us?
With over 20 years in Olympic weightlifting, strength training, nutrition coaching, and general fitness our team does its best to provide the audience with ultimate support and meet the needs and requirements of advanced athletes and professional lifters, as well as people who strive to open new opportunities and develop their physical capabilities with us.
By trusting the recommendations of our certified experts in coaching, nutrition, and sports training programming, as well as scientific consultants, and physiotherapists, we provide you with thorough, well-considered, and scientifically proven content. All the information given in the articles concerning workout programming, separate exercises, and athletic performance, in general, is based on verified data.
The product testing process is described in more detail here.
Author: Oleksiy Torokhtiy
Olympic Weightlifting Champion, PhD in Sport Science
Best Results: Snatch – 200 kg,
C&J – 240 kg
Oleksiy Torokhtiy is a professional athlete boasting 20 years of experience in Olympic weightlifting. With multiple European and World titles under his belt, he has showcased his prowess in two Olympic Games (Beijing 2008 and London 2012). Upon concluding his illustrious career, Oleksiy dedicated himself to coaching. By 2022, he had conducted over 200 weightlifting seminars worldwide. He is the visionary behind an international sportswear and accessories brand known for its motto, “Warm Body Cold Mind.” Additionally, he is an esteemed author and the creator of a series of training programs and eBooks.



Still have questions after reading our article? Unlock your full potential by engaging with our experts and community! Don’t hesitate — leave a comment below and Oleksiy Torokhtiy will provide a personalized answer and insights to help you reach your goals.