Can You Take Pre-Workout While Breastfeeding?
Author:
Unlock your full potential by engaging with our experts and community! Have questions about your fitness journey or looking for expert advice on weightlifting techniques? Don’t hesitate — leave a comment below and Oleksandr Maksymenko will provide a personalized answer and insights to help you reach your goals.
Torokhtiy is reader-supported. Some links are affiliate links, and we may earn a commission at no extra cost to you. See our disclosure page for details.
Before we delve deeper into the benefits and precautions of pre-workout supplements for nursing mothers, let’s address the big question: Can you take pre-workout while breastfeeding?
Many mothers wonder if pre-workout for breastfeeding is safe and if there are any potential risks associated with pre-workout when breastfeeding.
Breastfeeding women often struggle with low energy and stamina levels, making postpartum workouts challenging. Pre-workout supplements can enhance energy, focus, and performance during exercise, but concerns about their safety while breastfeeding leave many moms uncertain.
This article explores the benefits and precautions of using pre-workout supplements while breastfeeding, including non-stimulant options, and provides guidance on making informed choices to boost energy and stamina during postpartum workouts.
Can you take pre-workout while breastfeeding? – Pre-workout supplements can be safe for breastfeeding mothers if they carefully monitor caffeine intake and prioritize choosing products with safe, natural ingredients. Anyway, first you should consult with a qualified healthcare provider before taking any supplements while breastfeeding.

Is a Pre Workout While Breastfeeding Okay?
Pre-workout supplements are designed to improve athletic performance and increase energy levels during exercise. They usually contain a combination of caffeine, other stimulants and substances that increase physical efficiency.
DISCLAIMER
The content within this article cannot be amended, reproduced, distributed, transmitted or resold without direct written permission from the author and affiliates. The author cannot be held liable under any circumstances for possible damages, reparation and monetary losses as a result of the information within this article.
This article is not medical advice and is not intended to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent any disease, disorder, or medical condition. It should never replace any advice and treatment provided by your physician or licensed healthcare provider.
While there is limited research on the safety of pre-workout supplements for breastfeeding mothers, some ingredients commonly found in pre-workout supplements, such as caffeine, may pass into breast milk and affect the infant.
High doses of caffeine can cause irritability, restlessness, and difficulty sleeping in infants. A safe caffeine intake for breastfeeding women is about 300 mg per day of all foods and beverages.
Furthermore, the safety of other ingredients found in pre-workout supplements has not been extensively studied in breastfeeding mothers, so it is important to exercise caution and consult with a healthcare provider before taking any supplements.
Even then, you need to carefully study the components of the supplement and choose the safest options. Remember, breastfeeding mothers can benefit from a healthy diet that provides sufficient energy and nutrients for both the mother and the infant.
Eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats can help maintain energy levels and support athletic performance. Supplements can be helpful, but they are no substitute for a balanced diet or getting enough sleep.
1. When Is It Okay?
Choosing a pre-workout safe for breastfeeding is essential for nursing mothers, as some ingredients can be harmful to their babies. The safety of pre-workout supplements for breastfeeding moms largely depends on the ingredients and the amount of caffeine they contain.
Caffeine is a primary ingredient in most pre-workout supplements and can pass through breast milk, potentially causing adverse effects on your baby. Therefore, it’s crucial to monitor caffeine intake and choose products with safe ingredients.
2. When Is It Not Okay?
If you have any concerns or pre-existing medical conditions, consult with your healthcare professional before using any pre-workout supplements. Certain ingredients can interact with medications and medical conditions, causing harmful side effects.

3. If You’ve Had a C-Section
If you’ve had a C-section, it’s essential to prioritize recovery before considering pre-workout supplement usage. C-sections are major surgical procedures requiring significant healing time, usually at least six weeks before starting any exercise program or using pre-workout supplements.
When resuming exercise, start with low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or yoga, and gradually increase intensity as your body heals. Listen to your body and avoid any exercise causing pain or discomfort.
Once fully recovered, breastfeeding mothers should carefully choose pre-workout supplements with safe ingredients, avoid excessive caffeine and consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
4. If You’re Exercising Regularly
Adjusting intensity and frequency: Breastfeeding moms who are exercising regularly should adjust the intensity and frequency of their workouts based on their energy levels and their baby’s needs. Overexertion can lead to decreased milk supply, so it’s crucial to prioritize rest and recovery and avoid pushing yourself too hard.
✅ Eating a Balanced Diet for Safe Weight Loss
Many moms who are breastfeeding are eager to shed the extra weight gained during pregnancy. Regular exercise and a balanced diet are key to keeping your body healthy and happy.
Not only are these habits crucial for overall health and well-being, but they can also support healthy weight management in the long term. It’s important for breastfeeding moms who want to lose weight to approach weight loss with caution and prioritize their and baby’s health.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats can provide the energy and nutrients needed to support breastfeeding while also promoting weight loss.
Consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian for personalized recommendations and avoid rapid weight loss or extreme calorie restriction. Breastfeeding can affect a mother’s appetite, energy levels, and nutritional needs, making it important to set realistic goals and make adjustments as needed.
Avoiding extreme calorie restriction or rapid weight loss is crucial for safety, as it can be harmful to both the mother and her baby. Instead, a balanced diet and moderate physical activity should be used to create a calorie deficit.

✅ Monitoring Body’s Response
Breastfeeding moms should also pay close attention to their bodies’ responses to exercise and pre-workout supplements. If you experience any adverse effects like fatigue, dizziness, or lightheadedness, you should stop using the supplement and consult with your healthcare professional.
✅ Ensuring Sufficient Rest and Recovery
Rest and recovery are crucial for breastfeeding moms to maintain their energy levels and support their babies’ development. Aim to get seven to eight hours of sleep per night, and consider taking naps during the day when your baby sleeps.
✅ Staying Hydrated
Another important consideration when using pre-workout supplements while breastfeeding is hydration. Breastfeeding mothers need to drink plenty of water to maintain their milk supply and keep their bodies functioning optimally.
Dehydration can cause fatigue, muscle cramps, and decreased milk production. Drinking water before, during, and after exercise can help prevent dehydration and promote recovery.
Key Substances in Pre-workout and Breastfeeding
While dietary supplements can be an excellent addition to a healthy lifestyle, it’s important to note that they are not regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for safety or effectiveness before hitting the shelves.
Yes, FDA does monitor adverse effects, but it’s only after the supplements are already available to the public.
To ensure your safety, it’s crucial to research the ingredients in any dietary supplement and consult with a healthcare professional before use. Don’t take chances with your health – make informed decisions about the supplements you choose to take.

1. Caffeine
The limited high-quality data available makes it difficult to provide definitive recommendations on safe caffeine intake levels for breastfeeding mothers. A safe level of caffeine intake for most mothers is thought to be between 300-500 mg daily (and it’s better to stick to the lower limit).
Infants of mothers with very high caffeine intake, equivalent to 10 or more cups of coffee per day, have been reported to experience fussiness, jitteriness, and poor sleep patterns. Other sources of caffeine, such as energy drinks, cola, yerba mate, or guarana, may also have dose-related effects on breastfed infants.
2. Creatine
Used as a dietary supplement to increase muscle mass and improve exercise performance. Creatine is a normal component of human milk, supplying about 9% of the infant’s daily requirements.
In pre-workouts the creatine content is usually low, if you do not take extra creatine it should not be a problem. If you have concerns, avoid creatine or consult a healthcare professional.
3. Other ingredients
Beta-alanine, L-Citrulline and nitric oxide boosters. Although these substances show high safety for healthy people, they have not been extensively studied in lactating mothers. Some experts recommend avoiding these supplements until more data is available, and, once again, it is best to consult with your healthcare provider before doing so.
Supplements and Herbs in Pre-workout to Avoid When Breastfeeding
It’s crucial to avoid supplements that can negatively affect milk production, harm the baby, or cause adverse reactions. Fortunately, such components are very rarely included in pre-workouts, but we will still list some examples. Consider staying away from the following (this is not an exhaustive list):

1. Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha is an adaptogen that can help the body manage stress. However, it may also cause excessive drowsiness in infants. Therefore, it’s better to avoid ashwagandha supplements while breastfeeding.
2. Berberine/goldenseal
Berberine is a compound found in goldenseal, which is an herb used for various medicinal purposes. However, it may interfere with the baby’s immune system and lead to jaundice in some cases. It’s best to avoid goldenseal and berberine supplements while breastfeeding.
3. Bilberry
Bilberry is a fruit that is rich in antioxidants and can help improve vision. However, it may cause hypoglycemia in infants and negatively affect milk production. Therefore, it’s better to avoid bilberry supplements while breastfeeding.
Is Non-stim Pre-workout Safe for Breastfeeding Moms?
While non-stim pre-workouts are generally safe for healthy individuals and do not contain caffeine, some ingredients have not been thoroughly studied for breastfeeding women.
A breastfeeding-friendly pre-workout should not include any substances that might interfere with milk production or harm the baby, thus it’s essential to consider their ingredients and consult with a healthcare professional before use.
Let’s be transparent: in this section, we will not give typical recommendations; only a health care professional can give them personally. But let’s analyze a pre-workout with a good reputation, if it looks suitable for pre-workout for nursing moms.
Our Recommended Pre-Workout Pick
Pre-Workout Supplement Naked Energy
- Item Form: Powder
- Best For: Training Volume, Muscular Endurance, Reducing Fatigue, Enhanced “Pumping” Effect
- Flavor: Unflavored
- Special Ingredients: Beta-Alanine, L-Citrulline Malate
- Servings per Container: 50
- Serving: 5g
- Price Per Serving: ~$0.72
- Company Founded: 2014
- Recommended by Athletes: Daniel Victor
If you’re a breastfeeding mom looking for a pre-workout supplement that can help you improve exercise performance and mental focus, and promote faster recovery, Naked Energy could be a reasonable option.
With pure ingredients like creatine monohydrate, vitamin B3, B6, B12, beta-alanine, and more, Naked Energy provides a clean energy boost to help you perform at your best while ensuring your safety. Let’s explore the main ingredients closer:
1. Creatine Monohydrate
This naturally occurring compound is found in animal foods, such as red meat, pork, and fish, but is also a natural component of milk. Vegetarians, however, may consume less creatine from their diet, making it an ideal supplement for those looking to maximize their workout gains.
Nonetheless, it is also a natural component of milk. When consumed in a pre-workout supplement, which usually contains a fairly low dosage, there is little cause for concern. In case of any concerns, it is worth consulting a healthcare provider.
2. Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is essential for healthy red blood cell production, nerve function, and DNA synthesis. It may also improve energy levels and mood, which can be especially beneficial for breastfeeding moms who may experience fatigue and mood swings.
Vitamin B12 is typically safe for breastfeeding mothers in recommended doses, and many do not get enough of it with food.
3. Beta-Alanine
Beta-alanine is an amino acid that can increase muscular endurance and reduce fatigue during intense exercise. It may also help buffer lactic acid buildup, which can cause muscle soreness and fatigue.
The current data on beta-alanine suggests its safety in healthy individuals at recommended doses of 4-6 grams per day for healthy adults.
However, studies on the use of beta-alanine supplements by breastfeeding women are very limited, and therefore, caution is advised. While beta-alanine is naturally produced in the liver, it can also be acquired through the consumption of certain foods such as turkey, chicken, beef, pork, and fish.
However, to consume 3 grams of beta-alanine per day would require 2-3 pounds of meat and fish, which can be difficult to achieve through diet alone. Consequently, some individuals may turn to supplements to meet their daily beta-alanine requirements.
A serving of beta-alanine supplement often contains around 2 grams of beta-alanine, which is considered a reasonably safe dose, and is often not consumed every day. However, if any doubts arise about the safety of beta-alanine supplementation, consult with a healthcare professional.
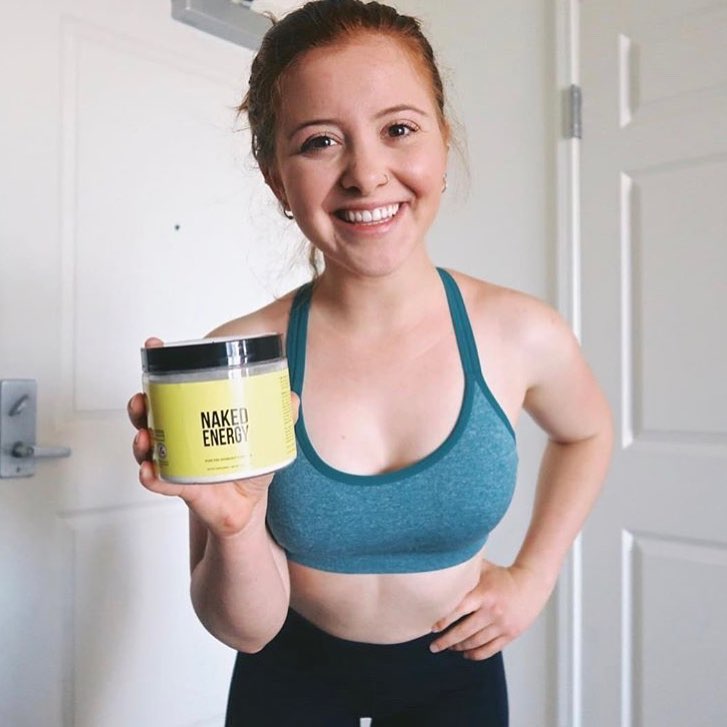

4. Caffeine
Caffeine is a natural stimulant that can provide mental focus, increased energy, and improved athletic performance. However, breastfeeding mothers should be cautious with their caffeine intake, as excessive amounts can cause irritability, restlessness, and sleep disturbances in infants.
The recommended maximum of caffeine intake for breastfeeding mothers is 300mg per day, and it’s better to stick to the lower limit.
Naked Energy supplement contains 200mg of caffeine, which is below the recommended maximum for breastfeeding mothers. To minimize potential adverse effects, it’s recommended to start with a lower dose of caffeine per day.
You can achieve this by starting with a half dose of the supplement or by reducing caffeine intake from other sources such as coffee or tea throughout the day. In case of any concerns or doubts, it’s recommended to consult with a healthcare professional.
Universal Guidelines: Maximizing Pre-Workout Benefits While Ensuring Safety
Breastfeeding mothers may find it challenging to balance the need for energy and stamina during postpartum workouts while ensuring the safety of their baby. Here are some guidelines for nursing moms to maximize the benefits of pre-workout supplements while prioritizing their child’s well-being:
1. Research Ingredients
Familiarize yourself with common pre-workout ingredients and their effects on breastfeeding. Choose supplements with ingredients that are safe for both you and your baby. Avoid ingredients known to have adverse effects on milk production or your baby’s health.
2. Monitor Caffeine Intake
Keep track of your daily caffeine consumption, including coffee, tea, and pre-workout supplements. Limit your caffeine intake to no more than 300 mg per day to prevent irritability and restlessness in infants.
3. Test Your Body’s Reaction
Start with a small dose of pre-workout and gradually increase it to assess your body’s reaction. This will help you determine the optimal dosage to provide the desired energy boost without causing any adverse effects on your baby or milk supply.
4. Maintain a Balanced Diet
Ensure that you’re consuming adequate calories and nutrients to support your body’s energy needs during breastfeeding and exercise. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats in your meals.
5. Prioritize Rest and Recovery
Getting sufficient rest is crucial for maintaining your energy levels and supporting your baby’s growth. Aim for at least 7-8 hours of sleep per night and consider taking naps when your baby sleeps. Incorporate rest days into your exercise routine to allow your body to recover and prevent overexertion.
FAQ
Does Pre-workout Affect Pump?
Many pre-workout supplements contain ingredients that increase blood flow and nitric oxide production, which can lead to greater muscle pump during exercise. However, the effect is generally temporary and varies depending on the individual and the specific supplement used.
How Long to Wait to Breastfeed after Drinking Pre-workout?
As a general recommendation, it is best to wait at least 2-3 hours after consuming pre-workout supplements before breastfeeding to ensure that the caffeine and other ingredients have had time to metabolize and pass through your system.
However, the specific waiting time may vary depending on the individual’s metabolism, the specific supplement used, and other factors.
Is Pre-workout Drinks Safe for Pregnancy?
The safety of pre-workout supplements during pregnancy largely depends on the ingredients and the amount of caffeine they contain. Caffeine is a primary ingredient in most pre-workout supplements and can cross the placenta, potentially affecting the baby’s heart rate and growth.
As long as careful attention is paid to caffeine intake and safe ingredients are selected, pre-workout supplements can be safely used by breastfeeding mothers with guidance from their healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pre-workout supplements can help breastfeeding moms boost energy and stamina, but it’s vital to consider caffeine intake, hydration, and ingredient safety.
By selecting safe alternatives and consulting healthcare professionals, nursing mothers can enhance their workouts without harming their babies while maintaining a balanced diet and appropriate exercise routines.
If you have any thoughts or additional information to share, please leave a comment below. We value your input and would love to hear from you!
Also read:
- Stim vs Non Stim Pre Workout
- Pre Workout With No Artificial Sweeteners
- Does Pre Workout Make You Gain Weight
- Can You Take Pre Workout Without Working Out
- How Long Does Pre Workout Stay In Your System
- Does Pre Workout Give You A Pump
- Does Pre Workout Help Build Muscle
- Nitric Oxide Supplements Guide
References:
- Effects of caffeine consumption on pregnancy outcome. A review. // Europe PMC: https://europepmc.org/article/med/3063816.
- Drugs and Lactation Database. Caffeine // National Library of Medicine: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501467/.
- The New Mother: Taking Care of Yourself After Birth // STANFORD MEDICINE CHILDREN’S HEALTH: https://www.stanfordchildrens.org/en/topic/default?id=the-new-mother-taking-care-of-yourself-after-birth-90-P02693.
- Nursing Your Baby What You Eat and Drink Matters // Eatright: https://www.eatright.org/health/pregnancy/breastfeeding-and-formula/nursing-your-baby-what-you-eat-and-drink-matters.
- Dietary Supplements: What You Need to Know // National Institutes of Health: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/WYNTK-Consumer.
- Effects of maternal caffeine consumption on the breastfed child: a systematic review // National Library of Medicine: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30294771/.
- Chemistry of Human Breast Milk-A Comprehensive Review of the Composition and Role of Milk Metabolites in Child Development // National Library of Medicine: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30247884/.
- Ashwagandha // WebMD: https://www.webmd.com/diet/supplement-guide-ashwagandha.
- Berberine // MedlinePlus: https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/natural/1126.html.
- Drugs and Lactation Database. Bilberry // National Library of Medicine: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501825/.
- Vitamin B12 // National Institutes of Health: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB12-HealthProfessional/.
- Photos are made by Torokhtiy Media team; Photo by @freepik, Freepik.com.
Why Trust Us?
With over 20 years in Olympic weightlifting, strength training, nutrition coaching, and general fitness our team does its best to provide the audience with ultimate support and meet the needs and requirements of advanced athletes and professional lifters, as well as people who strive to open new opportunities and develop their physical capabilities with us.
By trusting the recommendations of our certified experts in coaching, nutrition, and sports training programming, as well as scientific consultants, and physiotherapists, we provide you with thorough, well-considered, and scientifically proven content. All the information given in the articles concerning workout programming, separate exercises, and athletic performance, in general, is based on verified data.
The product testing process is described in more detail here.
Author: Oleksandr Maksymenko
Certified Sports Nutritionist,
MSc Sports Dietetics
Specializing in: Weight management, Fitness / Sports nutrition
Oleksandr is a professional fitness nutritionist certified by the Fitness Professional Association (FPA). He follows the principles of evidence-based dietetics and fosters a healthy relationship with food in his clients, ensuring there are no strict prohibitions on their favorite foods or frequent lapses. His primary goal is not only to achieve results for you but also to sustain them over the long term, all while enjoying tasty and delicious food.




Still have questions after reading our article? Unlock your full potential by engaging with our experts and community! Don’t hesitate — leave a comment below and Oleksandr Maksymenko will provide a personalized answer and insights to help you reach your goals.